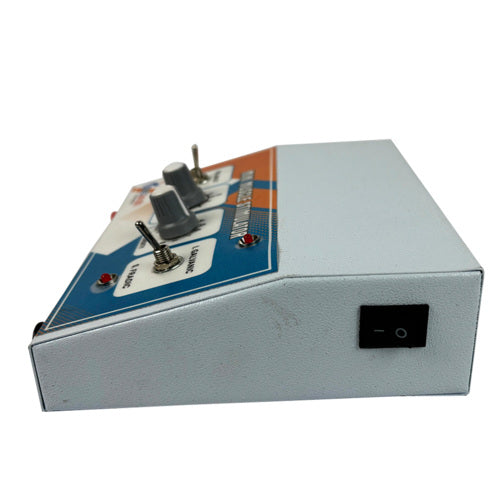
-
Experience precision tuning with our Tuning Fork Combo Set, including frequencies 128Hz, 256Hz, and 512Hz for various applications.Specifications:Combo comes with frequencies of 128Hz, 256Hz and 512Hz.High-Quality Material: Made from durable and resonant materials.Precision Tuning: Ideal for various medical and therapeutic uses.Compact and Portable: Easy...
- Rs. 413Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 736- Rs. 413
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 323Inclusive of all taxes
-
Neurological Knee Hammer Set – Comprehensive Reflex Testing Tools Product Overview: The Neurological Knee Hammer Set is a meticulously curated collection of reflex hammers and diagnostic tools designed for healthcare professionals to perform accurate neurological assessments. This set is essential for eliciting myotatic (muscle),...
- Rs. 1,379Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 2,024- Rs. 1,379
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 645Inclusive of all taxes
-
More sizes availableA tuning fork is a metal instrument with two prongs or tines and a handle. When hammered, tuning for ksvibrate at a specific frequency to generate a musical tone. The vibrations can be used to test a person's capacity to hear different frequencies of...
- Rs. 199Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 322- Rs. 199
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 123Inclusive of all taxes
-
The Taylor Reflex Hammer Elicits Myotatic And Plantar Responses With Less Effort And Greater Patient Comfort. The Precisely Balanced Handle Offers Increased Control Of Percussion Force The Weighted Chrome-Plated Handle Is Precisely Balanced For Increased Control Of Force In The Percussion. The Encircling Band...
- Rs. 183Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 367- Rs. 183
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 184Inclusive of all taxes
-
Utilizing the original design of Dr. John Madison Taylor, Latex Free Knee Hammer incorporates modern design and functionality for eliciting myotatic and plantar responses with less effort and greater patient comfort. The silicone triangular head has a beveled apex and base to elicit myotatic...
- Rs. 275Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 551- Rs. 275
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 276Inclusive of all taxes
-
A hammer is a diagnostic device used to trigger reflexes anddetect anomalies in the central nervous system. The thermoplastic-rubber triangular head of the reflexhammer with bevelled apex and base is used to induce myotatic reaction. Thesoft base and rounded tip are perfect for eliciting...
- Rs. 275Inclusive of all taxes
Rs. 460- Rs. 275
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 185Inclusive of all taxes
Recently Viewed Products
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
Medansh
Example product title
- Rs. 20Inclusive of all taxes
- Rs. 20
- Unit price
- per
Inclusive of all taxes
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.